CASE
6
Chest
CHEST 50 by Dr Sushen Kumar, Nanavati Superspeciality Hospital, Mumbai
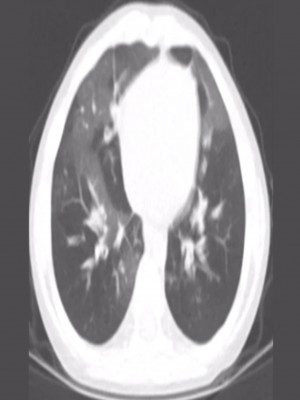
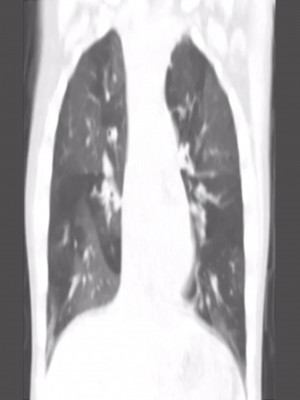
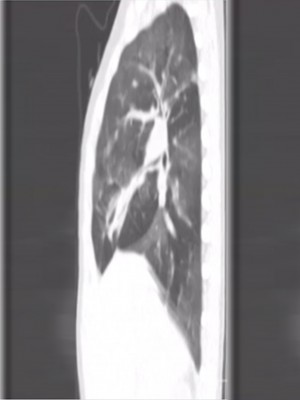
4 year old male with progressive shortness of breath.
History of hospitalization for pulmonary adenovirus infection at 10 months of age
Select option
- A - Bronchiolitis obliterans
- B - Congenital Lobar Emphysema
- C - Dependent opacities
- D - Broncho alveolar Carcinoma